2026 ውስጥ የየይዘት ደህንነት ለማሻሻል የሚሆኑ 10 ታላቅ ተግባራት
2026 ውስጥ የይለፍ ቃል security የሚሆኑ 10 የተመረጡ ተግባራትን ይፈልጉ። ኃይለኛ የይለፍ ቃል ማዘጋጀት፣ MFA እንዴት መጠቀም እና የዕውቀት አደጋዎች ከአካውንቶችዎ መከላከል ይማሩ።

የተመነጨ ማስተካከያዎች
በዚህ ዘመን የዲጂታል እጅግ የሚያስተዋወቅ በሆነ የገንዘብ ውሂብ እስከ የግል መረጃዎች ድረስ ይወስዳል፣ የይለፍ ቃል የመጀመሪያ መከላከያ ነው። ነገር ግን፣ በብዙ ድረ-ገጾች ላይ የሚያገኙ መረጃዎችን ወይም በቀላሉ ሊገኙ የሚችሉ የቃላት አሰባሰቦች የበለጠ ውህደት ይፈጥራሉ። የተለመዱ መንገዶች በብዙ ጊዜ የወረዳ ይመስላሉ እና የዘመናዊ የዲጂታል ደህንነት የሚያስቀርቡ የተወዳዳሪ ድርጅቶችን ማድረግ አልቻሉ። ይህ መመሪያ የተለመዱ ጥቅሶችን በማለፍ ወደ ዘመናዊ የይለፍ ቃል ደህንነት የሚያስተዋወቅ የተለያዩ የሚደርሱ የተግባር ዝርዝሮችን ይሰጣል።
የዲጂታል ሕይወትዎን ለመዝግብ የተለመዱ ዘዴዎችን እንደነዚህ በዝርዝር እንደሚኖሩ ይገናኛል። ይህ በታላቅ ደረጃ የተለያዩ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮችን ማዘጋጀት ይወዳድር፣ እና የእነዚህን ይለፍ ቃሎች በተመጣጣኝ መንገድ ማስተዳደር ይማሩ። የተለያዩ የይለፍ ቃል አገልግሎቶችን ይጠቀሙ፣ የይለፍ ቃል አስተዳደር በመጠቀም ወይም የተለመዱ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮችን ይቀይሩ፣ እና የፊሽንግ እና የመለያ እንደዚህ የሚኖሩ የተወሰኑ ድርጅቶችን ይረዳሉ። ከዚያ በተጨማሪ የእንደዚህ የተወሰኑ ድርጅቶችን ለመቀየር ይማሩ።
በዚህ ዝርዝር ውስጥ ተግባራዊ ምሳሌዎችን እና ዝርዝር ዝርዝሮችን እንደሚያቀርቡ ይቀርባሉ። የድር መሣሪያ መሳሪያዎች ይህን የደህንነት መርምር ይቀርባሉ፣ የShiftShift እንደ ተለያዩ የሚያቀርቡ የሚያስተዋወቅ የይለፍ ቃል መሳሪያ እና የአንደኛ አሰባሰቦች ይህን የደህንነት መርምር ይቀርባሉ። ይህ የደህንነት መመሪያ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮችን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮችን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮችን ይሰጣል።
1. ለእያንዳንዱ መለያ የተለየ እና የተረጋገጠ ይለፍ ቃል ይጠቀሙ
ለእያንዳንዱ የድረ-ገጽ መለያ የተለየ የተወዳዳሪ ይለፍ ቃል ማዘጋጀት የይለፍ ቃል ደህንነት የተለመዱ መርምሮች ውስጥ በተመለከተ የተለመዱ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ነው። የተለየ ይለፍ ቃል የመጀመሪያ መከላከያ እንደ ተለመዱ የተለመዱ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ነው፣ የተለየ ይለፍ ቃል የመጀመሪያ መከላከያ እንደ ተለመዱ የተለመዱ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ነው።
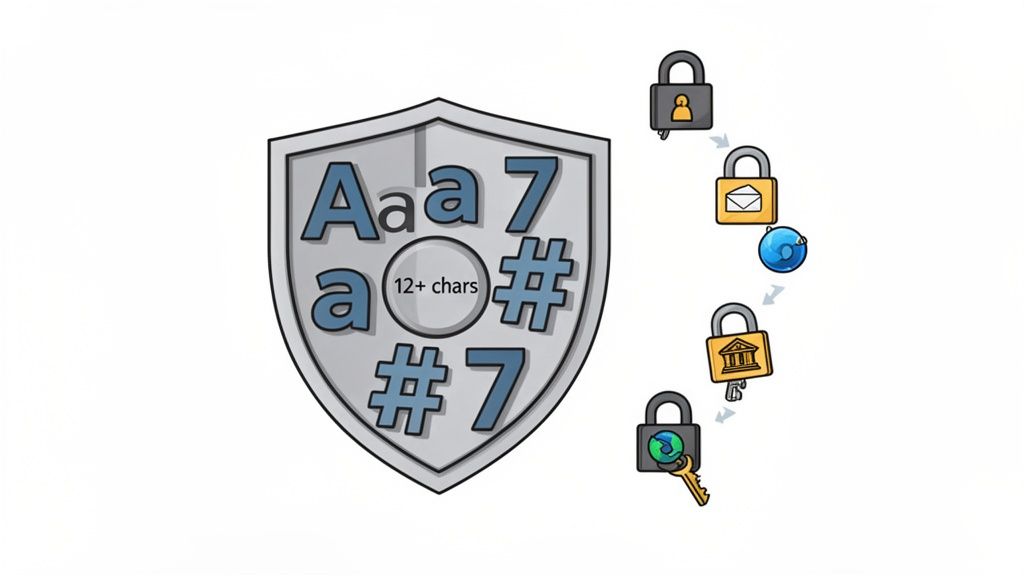
"የተለየ" የሚለው አንዱ እንደሆነ አስፈላጊ ነው። በብዙ አገልግሎቶች ውስጥ የተለየ ይለፍ ቃል ይጠቀሙ የሚለው የተለየ ይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል። አንድ አገልግሎት ሲታገኝ የተለየ ይለፍ ቃል ይጠቀሙ ይህን ይሰጣል። የMicrosoft የምርምር ይህን ይሰጣል፣ 99.9% የተገኘ መለያዎች ይህን ይሰጣል።
ይህን ዘዴ ለማድረግ እንዴት ይቻላል
የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
- የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል: የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
- የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል: የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
- የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል: የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
ለShiftShift አስተዳደር ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
2. የተለያዩ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል
ከዚያ በተጨማሪ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
ይህን ዘዴ ለማድረግ እንዴት ይቻላል
የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
- ይህን ይሰጣል: የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
- ይህን ይሰጣል: የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
- ይህን ይሰጣል: የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል።
2. የተለያዩ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል
ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።

ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
ይህን ዘዴ ለማድረግ እንዴት ይቻላል
ይህን ይሰጣል፣ የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም የይለፍ ቃል ዝርዝሮች ይሰጣል።
- ይህን ይሰጣል: ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም ይህን ይሰጣል።
- ይህን ይሰጣል: ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም ይህን ይሰጣል።
- ይህን ይሰጣል: ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም ይህን ይሰጣል።
ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ይህን ይሰጣል፣ ወይም ይህን ይሰጣል።
Store these codes in a secure, encrypted location like a password manager, but separate from the account password itself.For ShiftShift Extensions users, enabling MFA on your core accounts (like your Google or Microsoft account tied to the browser) is essential. It provides a robust safeguard, ensuring that the central hub controlling your browser extensions and their data remains exclusively yours.
3. Use a Reputable Password Manager
Using strong, unique passwords for every account is a core tenet of password security, but human memory can't keep up. A password manager solves this problem by securely generating, storing, and autofilling credentials. These tools act as an encrypted digital vault, requiring you to remember only one strong master password to access all your others, effectively resolving the conflict between security and convenience.
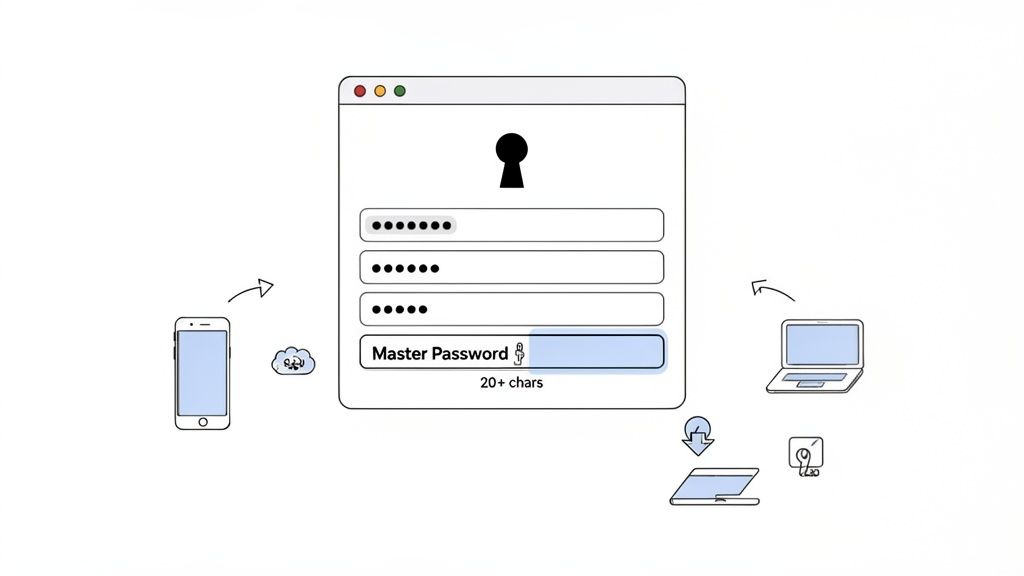
This approach is essential infrastructure for modern digital life, especially for developers and tech professionals who manage dozens or even hundreds of accounts across different services and environments. Instead of relying on insecure methods like spreadsheets or browser-based storage, a dedicated password manager uses robust, zero-knowledge encryption to protect your data. This means even the provider cannot access your stored credentials.
How to Implement This Practice
Choosing and correctly configuring a password manager is critical for establishing a secure digital foundation.
- Select a Trusted Provider: Look for managers with a strong reputation and transparent security practices. Options range from open-source choices like Bitwarden, enterprise-grade solutions like 1Password, to local, offline alternatives like KeePass.
- Create an Unbreakable Master Password: This is the single most important password you have. Make it a long passphrase of 20+ characters that is unique and has never been used anywhere else.
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Secure your vault by requiring a second verification step, such as an authenticator app or a physical security key, before granting access. This adds a critical layer of protection.
- Use the Built-in Generator: Let the password manager create cryptographically random passwords for all new accounts. This removes human bias and ensures maximum strength, a feature built directly into tools like ShiftShift's Password Generator.
Once you've chosen a password manager, familiarize yourself with essential password manager best practices to maximize its security benefits. Regularly audit your vault for weak, reused, or old passwords and update them promptly.
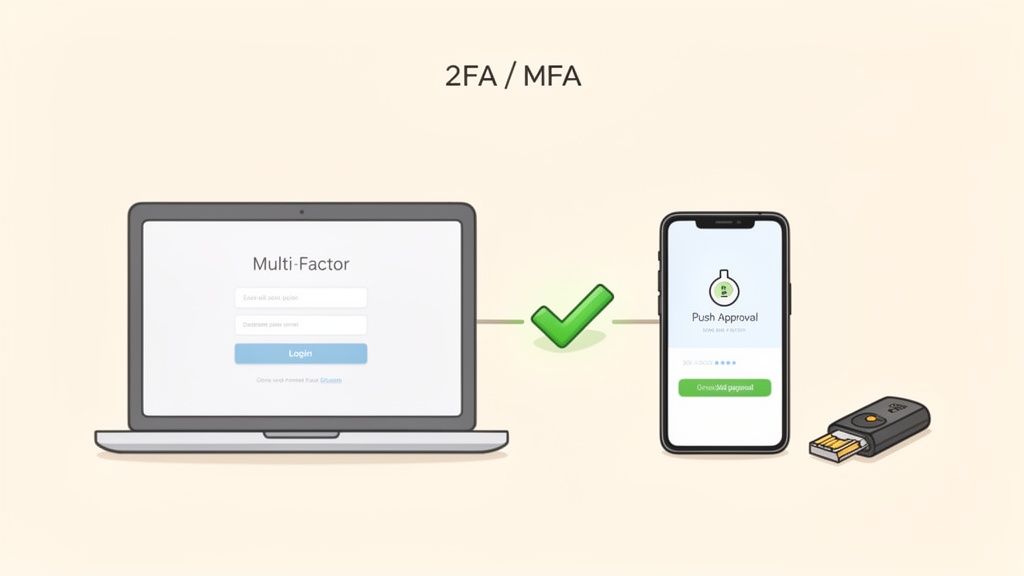
4. Enable Two-Step Verification on Email Accounts
Your email account is the master key to your digital life. It's the central hub for password reset links, security notifications, and sensitive communications. Securing it with more than just a password is one of the highest-impact best practices for password security you can adopt. Enabling two-step verification (2SV), also known as two-factor authentication (2FA), adds a crucial second layer of defense, ensuring that even if your password is stolen, your account remains inaccessible.
This method requires a second piece of information besides your password to grant access. This could be a code from an authenticator app, a physical security key, or a prompt sent to your trusted device. For high-value targets like your primary Gmail or Microsoft account, which can be used to reset passwords for nearly all your other services, implementing 2SV effectively neutralizes the threat of a simple password leak.
How to Implement This Practice
Setting up 2SV is a straightforward process that dramatically enhances security. The goal is to make it impossible for an attacker to log in without physical access to one of your devices.
- Prioritize Authenticator Apps Over SMS: While SMS-based 2SV is better than nothing, it's vulnerable to SIM-swapping attacks. Use a time-based one-time password (TOTP) app like Google Authenticator or Authy for a more secure verification method. Major providers like Google and Microsoft strongly support this.
- Register Backup Methods: Always set up more than one verification method. Register a backup phone number and generate a set of one-time recovery codes. Store these codes in a secure, encrypted location separate from your password manager, such as an encrypted file or a physical safe.
- Test Your Recovery Process: Before you desperately need it, test your 2SV and recovery methods. Ensure your backup phone number works and you know where your recovery codes are. Update this information annually or whenever you change devices to prevent being locked out of your own account.
5. Regularly Update and Patch Software
Effective password security extends beyond the password itself; it relies on the integrity of the software that handles your credentials. Regularly updating and patching your software is a critical, yet often overlooked, best practice for password security. Vulnerabilities in operating systems, browsers, and applications can be exploited by attackers to steal stored credentials, log keystrokes, or bypass authentication measures entirely.
Software updates frequently contain crucial security patches that close these known loopholes before they can be widely exploited. The infamous Log4Shell vulnerability in 2021, for example, affected millions of applications and allowed attackers to execute code remotely, highlighting how a single unpatched flaw can have catastrophic consequences. Keeping your software current ensures you are protected against the latest discovered threats.
How to Implement This Practice
Integrating software updates into your routine is a simple yet powerful security habit. The goal is to minimize the window of opportunity for attackers to exploit known vulnerabilities.
- Enable Automatic Updates: This is the most effective way to stay protected. Configure your operating systems (like Windows and macOS) and primary applications to install updates automatically. Modern browsers like Chrome and Firefox are designed to update silently in the background, a key feature for maintaining security.
- Regularly Check Browser Extensions: Extensions operate within your browser's security context and can have significant privileges. Manually check for updates to your extensions weekly by visiting your browser's extensions management page (e.g.,
chrome://extensions). This ensures that any discovered vulnerabilities are patched promptly. - Prioritize Operating System Patches: Your OS is the foundation of your device's security. Pay immediate attention to security patch notifications from your OS provider and install them as soon as possible. These updates often address system-level threats that could compromise all applications on your device.
For users of ShiftShift Extensions, maintaining an updated browser is paramount. Since the extension functions within Chrome's environment, its security is directly tied to the browser's integrity. A patched browser ensures the secure sandbox in which ShiftShift operates remains uncompromised, protecting your in-browser activities and data.
6. Avoid Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing attacks and social engineering are insidious threats that bypass technical defenses by targeting the human element. Instead of trying to crack a strong password, attackers manipulate you into giving it to them willingly. These schemes often use urgent or enticing language to create a sense of panic or opportunity, tricking you into clicking malicious links or divulging sensitive credentials. Even the most robust password and multi-factor authentication can be rendered useless by a convincing phishing scam.
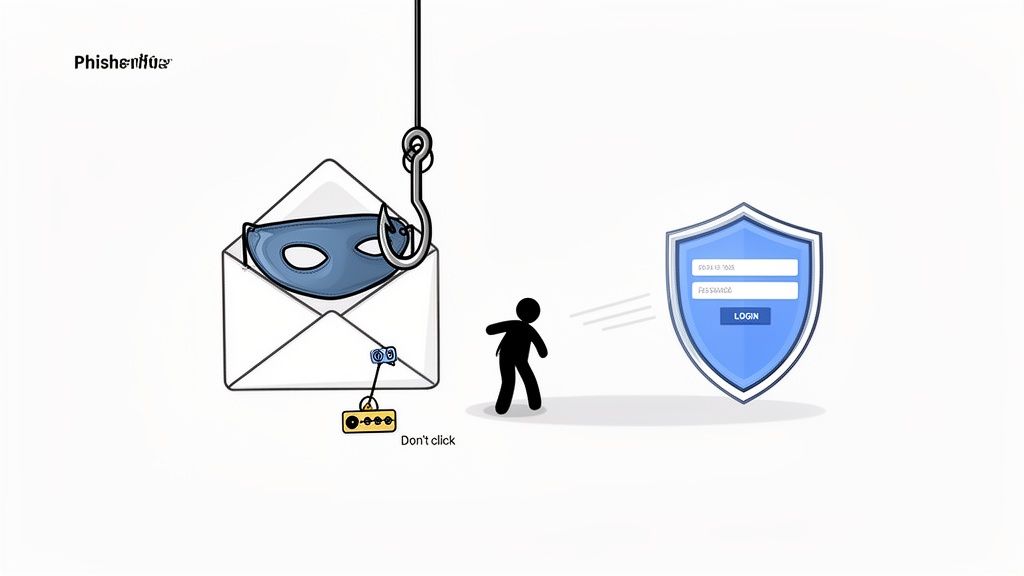
The prevalence of this tactic is staggering. Research from IBM reveals that human error is a factor in the vast majority of data breaches, highlighting how effective these psychological manipulations are. Successful spear-phishing campaigns against major tech companies and "CEO fraud" scams costing billions annually prove that no one is immune. Therefore, cultivating a healthy skepticism is one of the most critical best practices for password security.
How to Implement This Practice
The key to defending against these attacks is awareness and a consistent, cautious approach to unsolicited communication. Building a habit of verification can neutralize the threat before it escalates.
- Scrutinize Senders and Links: Always verify the sender's full email address, not just the display name. Before clicking any link, hover your mouse over it to preview the actual destination URL to ensure it matches the legitimate domain.
- Navigate Directly to Websites: Instead of clicking a link in an email that asks you to log in, open your browser and type the website's address manually. This completely avoids the risk of being sent to a spoofed login page.
- Be Wary of Urgency: Attackers create a sense of urgency to make you act without thinking. Be immediately suspicious of any message demanding immediate action, threatening account closure, or offering a too-good-to-be-true reward.
- Verify Through a Separate Channel: If you receive a suspicious request from a colleague or service, contact them through a known, separate communication method (like a phone call or a new message) to confirm its legitimacy.
- Use Browser Security Features: Modern browsers provide clear security indicators, such as the padlock icon for HTTPS. You can also enhance your security by using encrypted DNS, and you can learn more about how DNS over HTTPS strengthens your privacy and protects against certain attacks.
7. Monitor Accounts for Breach Notification and Suspicious Activity
Even the strongest password can be compromised if the service holding it suffers a data breach. Proactive monitoring is a critical layer of defense, allowing you to react quickly when your credentials are exposed. This practice involves regularly checking for your accounts in known breaches and keeping an eye on your account activity for any signs of unauthorized access.
This vigilance transforms your security posture from passive to active. Instead of waiting for a notification that your account has been misused, you can identify the initial exposure and take immediate action, such as changing your password, before any significant damage occurs. It's a key component of a comprehensive strategy for password security.
How to Implement This Practice
Effective monitoring combines automated tools with manual checks on your most critical accounts. The goal is to create a system that alerts you to potential threats as soon as they are discovered.
- Use Breach Notification Services: Regularly check your email addresses against databases of known breaches. Services like Troy Hunt's "Have I Been Pwned" are invaluable for this. Many modern password managers also integrate this functionality, automatically alerting you if a password you've stored has appeared in a data leak.
- Enable Login and Security Alerts: Configure your important accounts (like email, banking, and social media) to send you an alert via email or text message for new logins or suspicious activities. This provides real-time notification of potential unauthorized access.
- Review Account Activity Logs: Periodically check the login history and recent activity logs for your primary email and financial accounts. Look for unrecognized devices, locations, or access times. If you find anything suspicious, immediately revoke access for that device and change your password.
- Trust Your Tools: When using browser extensions like ShiftShift that handle various tasks locally, your data's security is paramount. Since these tools operate within your browser, ensuring no unauthorized activity is taking place is essential. You can learn more about how ShiftShift prioritizes user data by reviewing its comprehensive privacy policy.
8. Secure Password Recovery Methods and Backup Codes
Even the strongest password is of no use if you're locked out of your own account. Password recovery mechanisms, such as backup emails, phone numbers, and multi-factor authentication (MFA) backup codes, are your lifeline when primary authentication fails. However, these fallbacks are often the weakest link in your security chain, providing a backdoor for attackers to reset your password and seize control of your account.
Securing these recovery methods is a critical component of a comprehensive password security strategy. If an attacker compromises your recovery email, they can initiate a password reset for any account linked to it, bypassing your complex password and MFA. Similarly, stolen backup codes for services like Google or GitHub grant immediate access, rendering your primary two-factor device useless.
How to Implement This Practice
The goal is to treat your recovery methods with the same level of security as your primary credentials, ensuring they cannot be easily compromised or socially engineered.
- Secure and Isolate Recovery Channels: Use a dedicated email address for account recovery that is not publicly known or used for general correspondence. When setting security questions, provide false but memorable answers. For example, your "first pet's name" could be a random, unrelated word that only you know.
- Store Backup Codes Securely: When a service like Google provides you with backup codes for 2-Step Verification, do not store them in the same password manager as your primary password. Print them and keep them in a physically secure location, like a safe, or store them in an encrypted digital file separate from your main vault.
- Regularly Review and Test: At least once a year, review the recovery phone numbers and email addresses associated with your critical accounts. Ensure they are up-to-date and still under your control. It's also wise to periodically test the recovery process so you are familiar with it before an emergency occurs.
By fortifying your account recovery options, you close a common and often-exploited attack vector. This ensures that the only person who can regain access to your locked accounts is you, reinforcing the overall integrity of your digital identity.
9. Practice Secure Password Hygiene: Never Share or Reuse Passwords
Proper password hygiene involves the day-to-day habits of how you handle your credentials. It’s a core component of password security, focusing on preventing the behaviors that undermine even the strongest passwords. The two most critical rules of password hygiene are to never share your password with anyone and to never reuse it across different services. Sharing a password, even with a trusted colleague, creates an immediate security gap, as you lose control over who knows it and how it's stored.
Reusing passwords is a similarly dangerous practice. It creates a domino effect where a single data breach at one service can compromise all your other accounts. Attackers specifically use leaked credentials from one breach to launch credential stuffing attacks against other popular platforms, betting that users have recycled their passwords. Adhering to these hygiene principles is fundamental to maintaining a resilient security posture.
How to Implement This Practice
Good password hygiene is about building secure habits and leveraging the right tools to make those habits easy to maintain. The goal is to treat each password as a unique, confidential key.
- Use a Password Manager's Sharing Feature: If you need to grant someone access to an account, never send the password directly via email or messenger. Instead, use the built-in, secure sharing functionality of a reputable password manager, which allows for controlled, revocable access without exposing the raw credential.
- Implement Single Sign-On (SSO): For team environments, SSO is the gold standard. It allows users to access multiple applications with a single set of credentials, managed by a central identity provider. This eliminates the need for shared passwords entirely, as seen in AWS IAM best practices, which mandate individual user accounts over shared root credentials.
- Never Write Passwords Down Physically: Avoid storing passwords on sticky notes, in notebooks, or on whiteboards. These are easily lost, stolen, or photographed, completely bypassing digital security measures.
- Avoid Storing Passwords in Insecure Digital Locations: Do not save passwords in unencrypted text files, spreadsheets, or browser autocomplete on shared or public computers. እነዚህ ዘዴዎች በማርያው ወይም በወንጀል የተወሰኑ የአካል ግባት ላይ ትንሽ ወይም የማይኖር ጥበቃ ይሰጣሉ።
ለቡድኖች እና ግለሰቦች፣ በተለይም የሚያንቀሳቅሱ ውሂብ የሚያደርጉ እንደ አንደኛ የስራ አስተዳደር እና QA እንግነስ የሚጠቀሙ የShiftShift እንደ ማስተካከያ የሚገኙ የይለፍ ቃላት የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ጥበቃ ይወስዳሉ፣ ይህ የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር አይደለም። ይህ የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ይለፍ ቃላት የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ጥበቃ ይወስዳሉ፣ ይህ የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር አይደለም።
10. ተጠቃሚዎችን አስተምር እና የይለፍ ቃል የደህንነት ፖሊሲዎችን አቅርብ
የግለሰቦች የይለፍ ቃል ደህንነት ጥረቶች በአንደኛ የድርጅት ባህል እና ግልጽ መመሪያዎች በደግሞ ይማርከዋሉ። የይለፍ ቃል ፖሊሲዎችን መቅረብ እና ተጠቃሚዎችን በአሁኑ የሚኖሩ አደጋዎች ላይ አስተምር የደህንነት ከግለሰቦች ወደ ድርጅት የሚገኝ አንደኛ የድርጅት ባህል ይለዋዋጥ ይወስዳል። ይህ የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ይለፍ ቃላት የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ጥበቃ ይወስዳሉ፣ ይህ የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር አይደለም።
የበለጠ ፖሊሲዎች ከቀጣይ ስልጠና ጋር የተያያዘ የደህንነት ቅንብር ይፈጥራሉ። ተጠቃሚዎች የህጎች ወይም የይለፍ ቃል የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር ይለዋዋጥ ይወስዳሉ፣ ይህ የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር አይደለም። ይህ የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ይለፍ ቃላት የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ጥበቃ ይወስዳሉ፣ ይህ የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር አይደለም።
ይህን ዘዴ እንዴት እንደሚፈጽም
ዓላማው የተጠቃሚ የሚሆን እና የሚያስተዳድር ፖሊሲዎችን ማቅረብ ነው፣ ይህ የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር አይደለም። ይህ የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ይለፍ ቃላት የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ጥበቃ ይወስዳሉ፣ ይህ የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር አይደለም።
- የግልጽ ዘዴ ይፈጥሩ፡- የተለመዱ የይለፍ ቃል ፖሊሲ ይፈጥሩ። የዘመናዊ መመሪያዎች ይህ የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ይለፍ ቃላት የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ጥበቃ ይወስዳሉ፣ ይህ የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር አይደለም።
- የተደጋጋሚ የደህንነት ስልጠና ይከናወኑ፡- ወቅታዊ ወይም ወቅታዊ የደህንነት ዕውቀት ስልጠና ይከናወኑ። የተለመዱ የይለፍ ቃላት የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ጥበቃ ይወስዳሉ፣ ይህ የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር አይደለም።
- የድጋፍ መሣሪያዎች ይስጡ፣ እንግዲህ የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ይለፍ ቃላት የተዘጋጁ የበለጠ ጥበቃ ይወስዳሉ፣ ይህ የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር አይደለም።
- የአይነት የደህንነት ባህል ይኖር፡- የሚታወቅ የደህንነት ጉዳይ ይወስዳሉ፣ ይህ የሚያሳይ አስተዳደር አይደለም።
Top 10 Password Security Practices Comparison
| Practice | 🔄 Implementation Complexity | ⚡ Resource Requirements | ⭐ Expected Effectiveness | 📊 Typical Outcomes / Impact | 💡 Ideal Use Cases / Tips |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Use Strong, Unique Passwords for Each Account | Medium — requires discipline to create unique entries | Low — password generator recommended | ⭐⭐⭐ — greatly reduces reuse risk | Limits breach blast radius; prevents credential stuffing | Use for all accounts; prefer 12–16+ chars; use generator |
| Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) | Medium — per-account setup and backup planning | Moderate — authenticator apps, hardware keys, devices | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — blocks most account takeovers | Significantly lowers unauthorized access; aids compliance | Critical for admin/email/cloud; prefer hardware keys for high-value |
| Use a Reputable Password Manager | Low–Medium — initial setup and master password management | Moderate — manager app, possible subscription, sync devices | ⭐⭐⭐ — enables unique strong passwords at scale | Reduces reuse, offers breach alerts and secure sharing | Ideal for individuals and teams; enable MFA on manager |
| Enable Two-Step Verification on Email Accounts | Low — follow provider instructions | Low — authenticator app or backup phone | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ — secures primary recovery channel | Protects account recovery; prevents mass account takeover | Enable on all primary emails; use app/hardware over SMS |
| Regularly Update and Patch Software | Low — enable automatic updates and routine checks | Low — stable network, admin oversight | ⭐⭐⭐ — prevents exploitation of known flaws | Reduces malware/keylogger risk; maintains browser/extension security | Enable auto-updates; check extensions and OS regularly |
| Avoid Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks | Medium — ongoing training and user vigilance | Low — training materials, simulated tests | ⭐⭐⭐ — essential against human-targeted attacks | Fewer successful phishing incidents; stronger security culture | Train users, hover links, verify senders, run simulations |
| Monitor Accounts for Breach Notification and Suspicious Activity | Low–Medium — subscribe and review alerts regularly | Low — breach services, password manager alerts | ⭐⭐⭐ — enables rapid detection and response | Early containment; proactive credential changes after breaches | Check HIBP monthly, enable manager alerts, review login activity |
| Secure Password Recovery Methods and Backup Codes | Medium — configure multiple recoveries and secure storage | Low–Moderate — encrypted storage or physical safe | ⭐⭐⭐ — prevents unauthorized recovery and lockouts | Reliable recovery processes; fewer support escalations | Store backup codes offline/encrypted; register multiple contacts |
| Practice Secure Password Hygiene: Never Share or Reuse Passwords | Medium — policy adherence and cultural change | Low — policies + password manager / SSO tooling | ⭐⭐⭐ — limits insider risk and blast radius | Improved accountability; reduced shared-credential incidents | Use password manager sharing or SSO; prohibit plaintext sharing |
| Educate Users and Establish Password Security Policies | High — policy design, training, enforcement | Moderate–High — training programs, monitoring tools | ⭐⭐⭐ — sustains organization-wide best practices | Consistent behavior, compliance, faster breach response | Provide tools (managers/generators), regular training, clear policies |
From Practice to Habit: Integrating Security into Your Daily Routine
Navigating the digital world requires more than just knowing what to do; it demands consistent, conscious action. We have explored the ten pillars of robust password security, from the foundational principle of creating strong, unique credentials for every account to the strategic implementation of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) and the adoption of secure password managers. We've delved into the human element, recognizing the dangers of phishing and social engineering, and the organizational necessity of clear security policies. The journey through these best practices for password security reveals a clear truth: your digital safety is not a product you buy, but a process you cultivate.
The core challenge is transforming this knowledge from a checklist of practices into a set of ingrained, second-nature habits. The sheer volume of advice can feel overwhelming, but progress is made through incremental, high-impact changes. The goal is not to achieve perfection overnight, but to build a progressively stronger defensive posture.
Your Immediate Action Plan: Three Steps to a More Secure You
To make this transition from theory to reality, focus on the actions that provide the most significant security uplift for the least amount of initial effort. Consider this your "get started now" plan:
- Secure Your Digital Hub: Your primary email account is the key to your digital kingdom. If you do nothing else today, enable MFA or Two-Step Verification on this account. This single action creates a formidable barrier against unauthorized access, protecting the reset links and notifications for countless other services.
- Adopt a Centralized Vault: Choose and install a reputable password manager. Don't worry about migrating every single account at once. Start by adding new accounts as you create them and gradually move over your most critical logins, such as banking, social media, and primary work tools. This is the first step toward eliminating password reuse forever.
- Generate, Don't Create: Stop trying to invent complex passwords yourself. Humans are notoriously bad at creating true randomness. Instead, begin using a password generator for all new accounts and for any existing passwords you update. This ensures your credentials meet the highest standards of complexity and entropy without any mental effort.
Key Insight: The path to strong security isn't about a single, massive overhaul. It's about a series of small, consistent, and intelligent choices that compound over time, building a resilient and adaptive defense against evolving threats.
Beyond the Basics: Cultivating a Security Mindset
Once these foundational habits are in place, the broader principles we've discussed will become easier to integrate. You'll naturally become more skeptical of unsolicited emails, recognizing the hallmarks of phishing attempts. Regularly updating your software will become a routine task, not an annoying interruption. You'll think critically about the recovery methods you set for your accounts, opting for secure, pre-generated backup codes over easily guessed security questions.
Mastering these best practices for password security is more than just protecting data; it's about reclaiming control and peace of mind. It's about ensuring your personal information, financial assets, and digital identity remain yours and yours alone. By transforming these practices into daily habits, you are not just reacting to threats; you are proactively building a digital life that is resilient by design. The effort you invest today is a direct investment in your future security and digital well-being.
Ready to turn best practices into effortless habits? ShiftShift Extensions provides the essential in-browser tools you need, including a powerful Password Generator for creating uncrackable credentials on the fly. Streamline your security workflow and enhance your productivity by downloading the all-in-one toolkit from ShiftShift Extensions today.