How to Compare Two Text Files A Practical Guide for Developers
Learn how to compare two text files using powerful command-line tools, visual text editors, and convenient browser-based diff checkers. Master your workflow.

የተመነጨ ማስተካከያዎች
Comparing two text files might sound basic, but it's a skill that developers lean on every single day. Whether you're in the command line with a tool like diff, using a visual editor like VS Code, or just need a quick check in a browser-based utility, mastering this can save you from a world of headaches. It's how you spot rogue code changes, hunt down configuration errors, and make sure your data is exactly what you think it is.
Why Bother Mastering File Comparison?
Let's get real—"diffing" files is a constant in a developer's life. It’s the backbone of version control, the first step in debugging a mysterious issue, and the final check before pushing a critical configuration update. It’s less of a niche task and more of a fundamental part of maintaining code quality and keeping software reliable.
Think about it. From tracking down a single misplaced comma in a massive JSON file to reviewing a teammate's complex feature branch, a good file comparison gives you a clear, line-by-line story of what changed. It turns the abstract idea of "a few tweaks" into concrete proof of every addition, deletion, and modification. In a team setting where multiple people are touching the same code, that clarity is everything.
File Comparison Methods at a Glance
Before we dive deep, this table gives you a quick lay of the land. The right tool really depends on the job at hand.
| Method | Best For | Typical User | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Command-Line (CLI) | Scripting, automation, CI/CD pipelines, quick checks | System administrators, backend developers | Speed and scriptability |
| Code Editor | In-depth code reviews, daily development tasks | Any developer using an IDE/editor | Seamless workflow integration |
| Browser-Based Tool | Quick one-off comparisons, non-technical users | Anyone needing a fast, no-install comparison | Accessibility and ease of use |
Each of these approaches has its place, and knowing which one to grab is half the battle.
Choosing the Right Tool for the Job
The demand for these tools is no small thing. The global market for file comparison software was already valued between $1.2 billion and $1.72 billion in 2024. With DevOps practices becoming standard, that figure is expected to jump to over $5.6 billion by 2033. It’s clear this is a critical part of modern development.
If you're not sure where to start, this little decision tree can point you in the right direction.
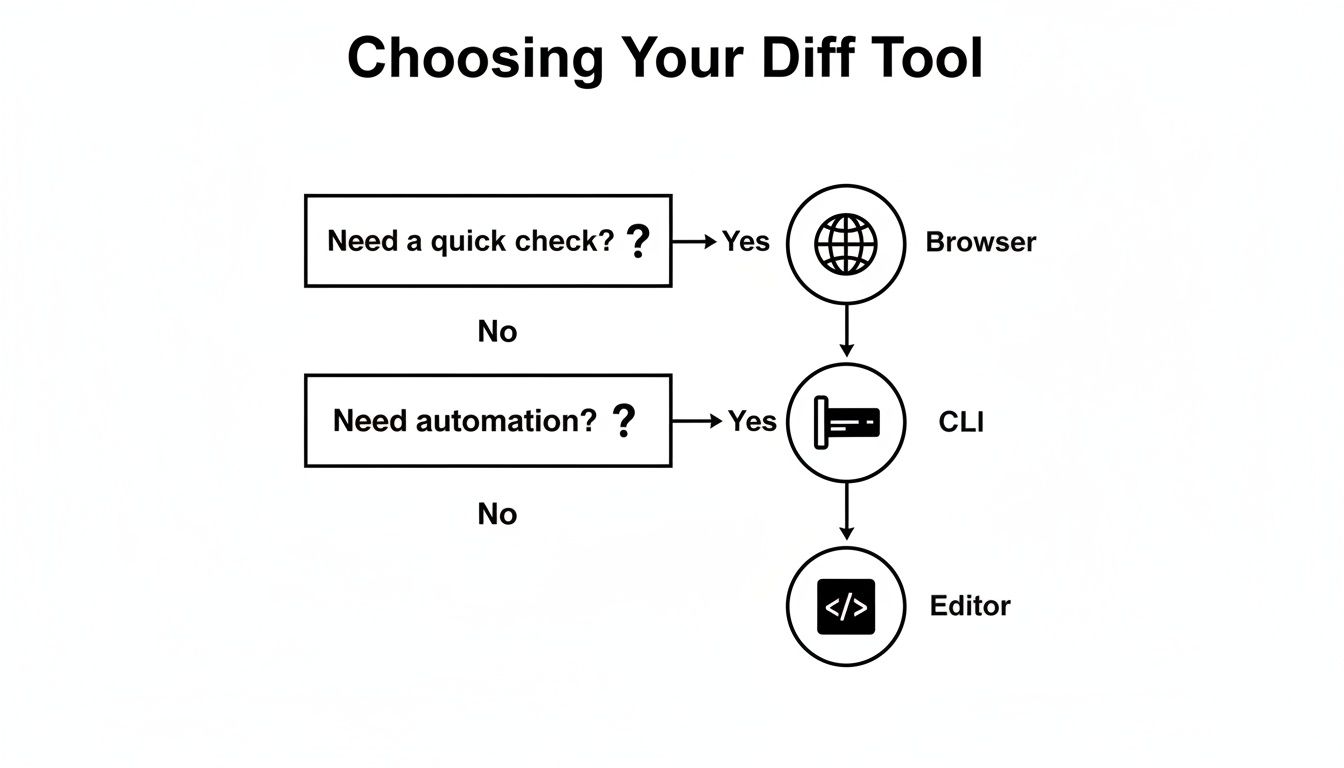
As you can see, the choice often boils down to a trade-off between speed, automation, and deep integration. We’re going to break down the three main ways to tackle this:
- Command-Line Utilities: These are the power tools. Think
diffandfc. They're built for automation and are essential for scripting and CI/CD pipelines, though they can feel a bit cryptic at first. - Visual Text Editors: This is all about convenience. Tools like VS Code bring intuitive, side-by-side comparisons right into the environment where you’re already working. It’s perfect for a seamless experience.
- Browser-Based Tools: Got two snippets of text you need to compare right now? This is your go-to. They require zero installation and are great for quick, one-off jobs. For more detailed analysis, a tool like Docuwriter's dedicated compare tool provides a powerful, web-based solution.
Picking the right approach is a huge part of what makes for effective developer productivity tools. It’s all about working smarter, not just churning out more code.
Mastering Command Line File Comparison
When you need pure speed, power, and automation, nothing beats the command line for comparing files. It cuts through the noise of a graphical interface, giving you a direct, scriptable way to see exactly what’s changed. This is the go-to method for developers, sysadmins, and anyone building automated checks into their CI/CD pipelines.
The command line isn’t just some old-school tool; it’s about raw efficiency. Modern file comparison utilities can scan and pinpoint differences in seconds, a job that would take hours to do by hand. This jump in capability is a huge win for catching errors and making sure your code or configurations are correct. You can find more on the impact of these tools in today's workflows at GlobalVision.
The Classic Diff Command on Linux and macOS
On any Unix-based system, which includes Linux and macOS, the undisputed king of file comparison is the diff command. At first glance, its output can seem a bit cryptic, but once you get the hang of it, you realize just how powerful it is. It tells you precisely which lines to add, delete, or change to transform one file into another.
Let's say you have two simple server configuration files, config.v1.txt and config.v2.txt.
Here’s config.v1.txt:
SERVER_NAME=prod-app
PORT=8080
ENABLE_SSL=false
And here’s config.v2.txt:
SERVER_NAME=prod-app-new
PORT=8080
ENABLE_SSL=true
LOG_LEVEL=info
If you pop open your terminal and run diff config.v1.txt config.v2.txt, you'll get a result that looks something like this:
So, what does that output mean?
1c1tells you that line 1 in the first file needs to be changed (c) to match line 1 in the second file.- Lines starting with
<are from the first file (config.v1.txt). - Lines starting with
>are from the second file (config.v2.txt). 3a4means that after line 3 of the first file, you need to add (a) the content from line 4 of the second file.
File Comparison in Windows with fc and PowerShell
Windows users aren't left out; they have a couple of great native options. The old-school choice is fc (File Compare), a trusty command that's been around for ages. It’s a straightforward tool that gets the job done by highlighting mismatched lines.
To compare our two config files, you’d simply run fc config.v1.txt config.v2.txt. The output is less detailed than diff, but it clearly shows you which lines don't match.
For a more modern and powerful approach, PowerShell gives us the Compare-Object cmdlet. This is a game-changer because it works with objects, not just plain text, making it incredibly flexible.
Pro Tip: I use PowerShell's
Compare-Objectfor all sorts of things beyond text files. You can compare the output of two different commands, check for differences in running processes, or even analyze complex data structures. It's a real workhorse.
Getting started with Compare-Object is easy. Just feed it the content of your files:Compare-Object (Get-Content config.v1.txt) (Get-Content config.v2.txt)
The output is much more intuitive than its predecessors. It uses side indicators (<= for the first file, => for the second) to point out exactly where the differences are, making it my preferred choice for any serious work inside the Windows ecosystem.
Using Your Text Editor for Visual Diffs
Let's be honest, while the command line is powerful, it’s not always the most intuitive way to see what's changed between two files. For many of us who practically live inside a text editor, switching contexts just to run a diff command feels like a workflow interruption. The good news? Your favorite editor probably has a fantastic, built-in tool to compare two text files visually.
Editors like Visual Studio Code and Sublime Text turn file comparison into a seamless, almost pleasant experience. Instead of squinting at command-line output, you get a clean, side-by-side view where every change pops. Additions, deletions, and modifications are highlighted in easy-to-understand colors, which is a lifesaver during code reviews or late-night debugging sessions.
Comparing Files in Visual Studio Code
VS Code’s diffing tools are top-notch, mainly because they’re baked right into its core Git integration. You don't even need to hunt for an extension to get started; it's all there out of the box.
Getting a comparison up and running is incredibly simple:
- Head to the File Explorer pane in your VS Code project.
- Find the first file, right-click it, and choose Select for Compare.
- Now, find the second file, right-click it, and hit Compare with Selected.
That's it. VS Code immediately opens a dedicated diff editor. This view is more than just a simple side-by-side; it highlights the exact characters that have changed within a line, not just the entire line itself. Trust me, that level of detail is a massive help when you're trying to spot a sneaky typo or a missing comma.
The view below is a perfect example of what you'll see when comparing changes in a Git-tracked file.
The visual language is clear: red on the left for removed lines, green on the right for added lines. You get an instant understanding of what’s been modified without needing to decipher any complex symbols.
Here's a tip from experience: When you're in VS Code's diff view, look for the little plus and minus icons next to each change. These let you stage or revert individual lines or blocks of code. It's an incredibly useful feature for building clean, precise commits.
Enhancing Sublime Text with Packages
Sublime Text has a massive following for its speed and clean interface. While it doesn't have a diff tool built-in quite like VS Code, it’s easily extended. To get the best experience here, you’ll want to install a package. The go-to choice for years has been Sublimerge, a powerful package that adds professional-grade diff and merge capabilities right into the editor.
Once you have a tool like Sublimerge installed, the workflow will feel very familiar:
- Select the two files you want to compare (or even just two selections of text).
- Launch the comparison, which opens a two-pane view (or even a three-pane view for more complex merges).
- From there, you can jump between differences and push changes from one file to the other with a click.
This approach is ideal for developers who love Sublime’s performance and have a highly customized setup. By adding a dedicated package, you can compare two text files quickly and accurately without ever breaking your coding rhythm.
Browser-Based Tools for On-the-Fly Comparisons
Sometimes, you just need a quick check. You don't need to fire up a terminal or launch a full-blown code editor; you just need to see the difference between two blocks of text right now. This is where browser-based tools come in, offering instant diffing power on any machine with an internet connection.
This approach is my secret weapon for those one-off tasks. I use it constantly when I’m helping a colleague on their machine or working from a computer where I can't just install my usual software. Online diff tools get you straight to the point without any setup.

Why Choose a Browser Tool?
The biggest draw is pure convenience. There's zero installation required. You can go from needing a comparison to seeing the results in seconds, not minutes. That kind of accessibility is a lifesaver for quick checks and impromptu debugging.
Plus, you get universal cross-platform compatibility. It makes no difference if you’re on Windows, macOS, or a Linux box. If you have a web browser, the tool works the same everywhere. For teams spread across different operating systems, that consistency is a huge win.
I’ve lost count of the number of times a browser diff has saved me. When I’m pulling a configuration snippet from a tutorial or a Stack Overflow answer, I’ll paste it and my own version into a browser tool. It instantly flags any typos or subtle formatting differences. It’s a simple sanity check that prevents a world of frustration.
Quick Guide: ShiftShift Extensions in Action
The workflow is built for speed. Let’s look at the Text Comparison tool in the ShiftShift Extensions suite. It couldn't be simpler: you paste your original text in one pane and the new text in the other.
Instantly, you get a side-by-side view with clear color-coding that highlights what’s been added or removed. This immediate feedback is what makes it so useful. You can see precisely which lines changed and even get real-time stats on character and word counts.
Here’s what makes a good browser-based tool stand out:
- Privacy is paramount. A common worry with online tools is where your data goes. The best browser extensions, including ShiftShift, do all the processing locally on your machine. Your text is never sent to a server, which is essential when you're working with anything sensitive.
- Works offline. Since the logic runs in your browser, a stable internet connection isn't required after the initial page load. This makes it a surprisingly reliable tool, even when your connection is spotty.
- Part of a toolkit. The most effective tools are often part of a larger ecosystem. For web developers, having a diff utility alongside other handy tools in one extension is a major workflow boost. You can learn more about similar Chrome extensions for web developers that take this integrated approach.
Ultimately, browser-based diff tools fill a vital niche. They offer a secure, accessible, and hassle-free solution when you don’t need the heavy-duty features of a dedicated application.
Comparison of Diff Tool Types
Choosing the right tool depends entirely on your situation. A command-line utility is perfect for automation, while a text editor offers deep integration. A browser tool, however, wins for speed and convenience. This table breaks down the key differences to help you decide.
| Feature | CLI Tools (e.g., diff) | Text Editors (e.g., VS Code) | Browser Tools (e.g., Online Diff) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Requires terminal access; installed on system | Requires editor installation and configuration | Instantly accessible via any web browser |
| Speed for Quick Tasks | Fast for experienced users, but has a learning curve | Slower; requires opening an application and files | Fastest; just paste text and see results |
| Installation | Often pre-installed on Linux/macOS; manual on Windows | Required on all platforms | Zero installation needed |
| User Interface | Text-based output; can be hard to read | Rich, graphical side-by-side view with syntax highlighting | Simple, intuitive graphical side-by-side view |
| Automation/Scripting | Excellent; designed for scripting and pipelines | Limited to editor-specific tasks and extensions | Not suitable for automation |
| Privacy | Excellent; all processing is local | Excellent; all processing is local | Varies; reputable tools process locally, others use servers |
| Best For | System admins, automated workflows, Git integration | Developers, writers, detailed code reviews, project work | Quick checks, non-technical users, temporary or shared systems |
As you can see, each category has its strengths. For those moments when you just need a quick answer without any fuss, a browser-based tool is often the smartest and fastest choice.
Navigating Advanced Diffing Scenarios

Knowing the basics of how to compare two text files is a great start, but real-world work is messy. You’ll quickly find that many differences a tool flags aren't meaningful content changes at all. They’re often just pesky formatting quirks.
These "invisible" differences can send you down a rabbit hole, hunting for a bug that isn't there. Three common culprits are behind this chaos: whitespace, character encoding, and line endings. A single trailing space, a tab instead of spaces, or a file saved as UTF-8 while another is in ASCII can make two functionally identical files look wildly different to a standard diff tool.
This is where you need to get smarter than your tools. By learning how to tell them to ignore these trivial variations, you can cut through the noise and focus on the substantial changes that actually matter.
Handling Whitespace and Encoding Conflicts
I’ve lost count of how many times whitespace has caused confusion, especially when working on a team where everyone has different editor settings. One person's IDE might add trailing spaces, while another's converts tabs to spaces. To a diff tool, these are all legitimate changes.
Fortunately, most command-line tools have flags to handle this. The diff command, for example, has the -w or --ignore-all-space flag. Running diff -w file1.txt file2.txt tells the tool to completely disregard whitespace differences, giving you a much cleaner output that highlights only the real modifications.
Character encoding is another sneaky one. If one developer saves a file with Windows-style CRLF (\r\n) line endings and another uses Unix-style LF (\n), a diff tool will report that every single line is different. Most modern text editors and visual diff tools have settings to either normalize line endings on the fly or ignore them during a comparison.
A pro tip for anyone working in a team is to establish a
.editorconfigfile in your project's root directory. This simple configuration file enforces consistent coding styles, including character sets and line endings, across different editors and IDEs, preventing most of these issues from ever occurring.
Comparing Huge Files and Entire Directories
What about when you need to compare massive log files that are several gigabytes in size? Trying to load them into a standard text editor or a visual diff tool is a sure-fire way to freeze your machine. For these heavy-duty jobs, command-line utilities are your best friends because they process files line-by-line instead of trying to load everything into memory.
When dealing with huge files, you can still use diff, but a smart move is to pipe its output to a pager like less for easier navigation.diff hugefile1.log hugefile2.log | less
This simple but effective trick lets you scroll through the differences smoothly without overwhelming your terminal or your system's memory.
Now, if you need to find changes across an entire project, comparing files one by one just isn't an option. This is a perfect job for recursive directory comparison. The diff command makes this incredibly easy with the -r (or --recursive) flag.
Just run this command to see all the differences between two versions of a project folder:diff -r project_v1/ project_v2/
The output will clearly list which files are unique to each directory and then show a standard diff for any file that exists in both but has different content. For developers, this is an indispensable command for auditing changes between branches or deployments. And if you just need a quick, visual way to check text snippets, you can find a guide to compare text online for free that works great for smaller tasks.
Common Questions About Comparing Files
Once you get the hang of basic file comparisons, you'll start bumping into more specific, real-world problems. This is the fun part—it's where you move from just knowing the commands to truly understanding the craft. Let's dig into some of the most frequent questions that come up when you start making these tools a part of your everyday work.
These aren't just about spotting a changed line anymore. We're talking about filtering out noise, untangling complex edits from multiple people, and even dealing with files that aren't plain text. Mastering these nuances is what makes you fast and effective.
How Can I See Only the Differences?
Sometimes, the full diff output is just... loud. When you’re staring at two massive log files where only a handful of lines have changed, scrolling through thousands of identical lines is a waste of time. You need a clean, concise report of only what’s different.
This is where command-line tools really shine. The classic diff command with the unified format flag (-u) is already pretty good at focusing on the action. But for an even cleaner view, you can tell it to hide everything that's the same.
The --suppress-common-lines option is a fantastic way to do this. It strips out all the matching lines, leaving you with a focused list of additions, deletions, and modifications. It’s perfect for generating a quick summary or patching a file.
What About a Three-Way Merge?
A simple two-way comparison is great for tracking changes between "before" and "after." But in the real world of team projects and version control systems like Git, things get more complicated. You're often faced with a three-way merge.
This situation involves three distinct files:
- Base: The original file, the common ancestor before anyone made changes.
- Mine: Your version of the file, containing your edits.
- Theirs: Your teammate’s version, with their separate set of edits.
A three-way merge tool doesn't just compare "Mine" and "Theirs." It uses the "Base" file as a reference point to intelligently weave together both sets of changes. This is the magic behind how Git handles merges automatically and, more importantly, how it pinpoints conflicts that need a human to resolve. When you run git mergetool, it often fires up a visual diff editor (like the one in VS Code) specifically set up for this task, making it way easier to untangle overlapping changes.
The real power of a three-way merge is context. It moves beyond asking, "Are these two files different?" and instead asks, "How have these two files diverged from their shared origin?" That context is what makes safe, automated merging possible.
Can I Compare Binary Files Like Word Docs?
The tools we've covered so far are built for plain text. If you try to run diff on a Microsoft Word document (.docx) or a PDF, you'll probably just get a blunt message like, "Binary files a and b differ," with zero helpful details.
That's because these file formats are more than just text. They're complex containers with styling, metadata, and all sorts of structural information that a simple text tool can't understand. To properly compare them, you need software that speaks their language.
For example, Microsoft Word has its own built-in "Compare Documents" feature, and Adobe Acrobat Pro can do the same for PDFs. These tools are designed to parse the internal structure and can show you changes in formatting and images, not just the text.
Ready to simplify your daily comparisons? ShiftShift Extensions offers a powerful, browser-based Text Comparison tool that's perfect for developers, writers, and anyone needing a quick, secure diff. Get instant, side-by-side results without ever leaving your browser. Download it from shiftshift.app and see the difference.