How to Fix Upload Speed and Stop Lagging Behind
Tired of slow uploads? Learn how to fix upload speed with our guide, covering hardware tweaks, software optimization, and when to call your ISP.

Before you start tearing your hair out or messing with router settings, let's get a clear, honest picture of your internet's current performance. The very first thing you need to do is run a proper speed test. I'm not talking about a quick check while ten browser tabs are open and Netflix is streaming in the other room.
We need a clean, controlled test. This means pausing any downloads, closing out of background apps, and, most importantly, plugging your computer directly into your router with an Ethernet cable. This gives us a solid baseline number—the ground truth of what your connection can do. It's the only way to know if the changes you make later are actually working.
Pinpointing the Real Cause of Slow Uploads
You can't fix what you can't measure. Trying to boost your upload speed without knowing where you're starting from is just guesswork. You might get lucky, but you won't know why something worked. The goal here is to get an unbiased measurement of your internet performance, completely free from the usual household interference.
Establish a Clean Testing Environment
First things first, let's eliminate all the usual suspects that eat up your bandwidth. Before you even think about running a speed test, shut down every single program on your computer that uses the internet.
I’m talking about everything:
- Cloud-syncing services like Dropbox, Google Drive, or OneDrive.
- Video and music streaming apps.
- Even those extra browser tabs you have open.
These things are notorious for silently munching on your upload bandwidth in the background, which will absolutely skew your test results.
Pro Tip: A reliable speed test demands a sterile environment. Any background activity competes for a slice of your bandwidth, which makes it impossible to diagnose the actual problem.
Now for the most important part: go wired. Wi-Fi is great for convenience, but it's terrible for accurate speed testing. It's easily disrupted by walls, other electronics, and even your microwave. To see the real speed your internet service provider is delivering, you have to connect your computer directly to your router with a good old-fashioned Ethernet cable. This direct line is the gold standard for an accurate reading.
This simple process—connecting via Ethernet, running a test, and looking at the numbers—is the foundation for everything else we're going to do.
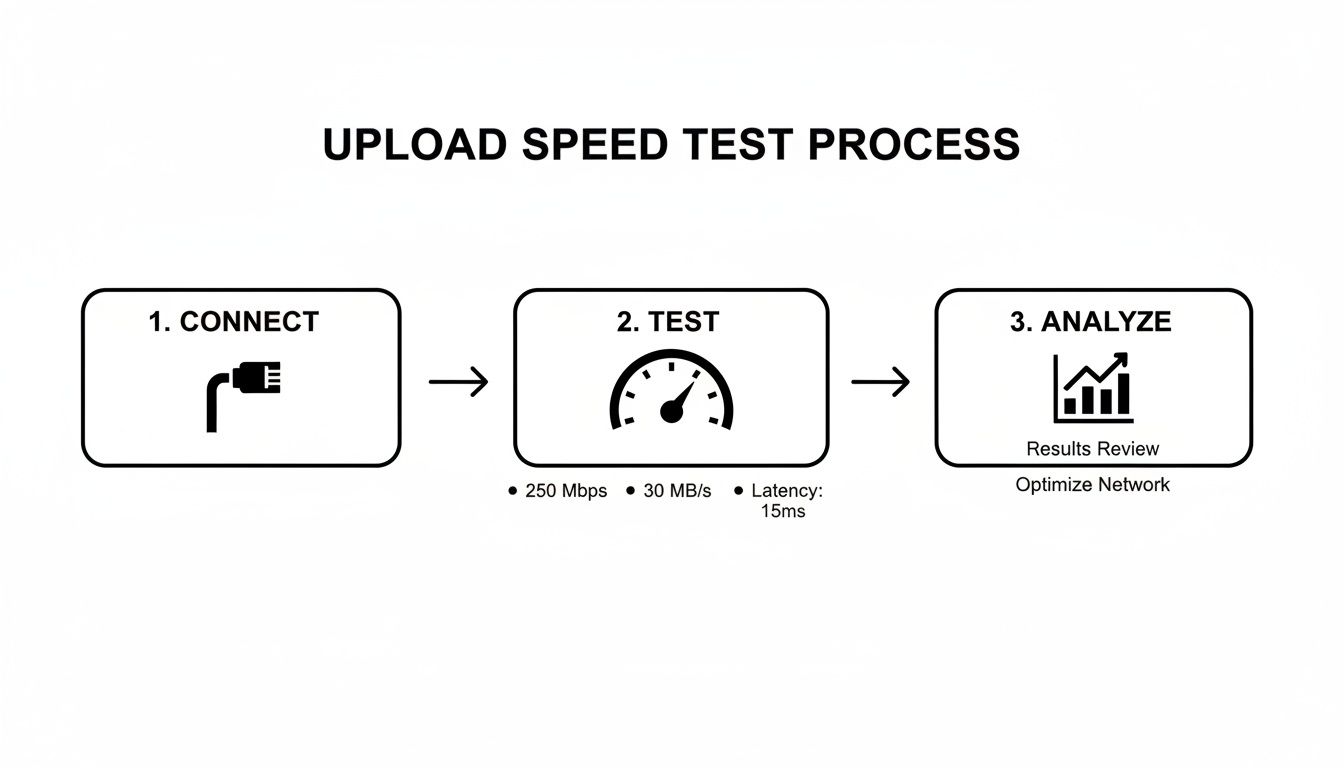
Following this workflow ensures you get a pure measurement of your connection's capability before you start tweaking settings.
Interpreting Your Speed Test Results
Okay, you've run the test and have your numbers. Now what? Pull up your internet plan details and compare what you're getting to what you're paying for.
It's completely normal for your actual speeds to be a little under the advertised "up to" number. But if you see a huge gap, that's your first major clue. For instance, if you're paying for 20 Mbps upload but your wired test only shows 5 Mbps, you’ve just found a concrete problem to solve.
Having this baseline data is your most powerful tool. For a deeper dive into network performance fixes, you can explore how to improve upload speed for gaming and streaming.
Start with the Obvious: Your Hardware and Connection

Before you start messing with complicated software settings, let's look at the physical stuff. I've found that some of the biggest speed boosts come from simple hardware tweaks that anyone can do. These are always my first go-to checks.
If there's one thing you do, make it this: get off Wi-Fi and plug in an Ethernet cable. I know, Wi-Fi is easy, but it's a nightmare for uploads. The signal gets chewed up by walls, household appliances, and even your neighbor's network. Uploading needs a rock-solid data stream, and Wi-Fi just isn't built for that kind of stability.
An Ethernet cable creates a direct physical link from your computer to your router. No signal drop, no interference. If you're live streaming, hopping on video calls, or trying to send massive files, a wired connection is non-negotiable for consistent performance.
Have You Tried Turning It Off and On Again? (The Right Way)
It’s a cliché for a reason. Power cycling your modem and router can work wonders. These little boxes are running 24/7 and, just like any computer, they can get bogged down with memory leaks and weird glitches that kill your speed.
But just flicking the power switch off and on isn't enough. There's a right way to do it:
- Start by unplugging the power cords from both your modem and your router.
- Now, go make a cup of coffee. Seriously, wait at least 60 seconds. This gives the internal capacitors time to fully discharge and completely clear the device's memory.
- Plug the modem back in first. Wait patiently for all the lights to turn solid green or blue. You're looking for the power, receive, send, and online lights to stabilize.
- Once the modem is happy, plug the router back in and let it fully boot up.
This little ritual forces each device to get a fresh handshake with your internet provider and can instantly fix upload problems caused by hardware fatigue.
A proper power cycle isn't a quick flick of a switch. It’s a full hardware reset that wipes out performance-sucking errors that have built up over time in your modem and router.
Where You Put Your Router Matters
Okay, so maybe a wired connection isn't an option for every device. In that case, where you place your router is everything. Remember, Wi-Fi is just a radio signal, and it hates obstacles. Thick walls, metal filing cabinets, and even fish tanks can wreck your signal.
For the best coverage, put your router out in the open, in a central spot in your home. Get it up high—on a shelf instead of on the floor. And keep it away from other electronics that can cause interference, like microwaves, baby monitors, and cordless phones.
You'd be surprised how much better your connection can get just by moving the router a few feet. It can be useful to take screenshots of your signal strength in different spots to see what works best. If you need a good tool for that, check out this guide on finding a great free Snagit alternative.
Look for Bandwidth Hogs on Your Own Devices
Sometimes the biggest bottleneck isn't your ISP or your router; it's the very device you're using. Your computer is a constant hum of activity, and many of those background applications are quietly fighting for their share of your upload bandwidth.
Think about all the software running that you're not actively using. Cloud storage services like Dropbox, Google Drive, or OneDrive are prime examples. Their main purpose is to keep your files in sync, which means they are often uploading data in the background. When you suddenly need that bandwidth for a video call or a large file transfer, you're left competing with your own software.
How to Find and Manage Bandwidth-Hungry Apps
Your first step is to play detective and figure out what's secretly eating up your connection. Luckily, your computer has built-in tools for this exact job.
- On a Windows PC, pull up the Task Manager by pressing Ctrl+Shift+Esc.
- On a Mac, you'll want to open the Activity Monitor, which lives in your Utilities folder.
Once you have the tool open, find the "Network" column. Sort it by "Send" or "Sent Bytes" to bring the biggest offenders right to the top. It's often surprising to see a software updater, a backup service, or even a browser extension consuming a huge chunk of your upstream connection.
When you've found a culprit, you have a couple of straightforward options:
- Temporarily shut it down. If you need every bit of speed for a specific task, simply close the applications that are consuming the most bandwidth.
- Tweak the settings. For apps that run all the time, like cloud sync tools, dig into their settings. Most let you pause syncing or schedule it for times when you're not using your computer, like overnight.
It’s easy for background processes to quietly consume your upload bandwidth without you even realizing it. The table below breaks down some of the most common culprits and gives you practical ways to manage them.
| Bandwidth Hog | Typical Impact | How to Manage |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Storage Sync (e.g., Dropbox, Google Drive) | High and constant. Uploads new or changed files automatically. | Pause syncing during important tasks or schedule it for off-peak hours in the app’s settings. |
| Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Software (e.g., BitTorrent) | Very High. Actively uploads ("seeds") file parts to other users. | Set upload speed limits within the application or close it completely when you need bandwidth. |
| Automatic Software Updates | Sporadic but High. Can start a large upload without warning. | Disable automatic updates in favor of manual checks, or schedule them for a specific time. |
| Online Backup Services | High. Runs in the background, uploading file backups to the cloud. | Schedule backups for late at night or weekends when you’re not actively using your connection. |
| Streaming/Gaming Overlays (e.g., Discord, Twitch) | Moderate to High. Can upload voice data, video, or gameplay streams. | Disable automatic streaming features and check settings for video quality and bitrate. |
By keeping an eye on these processes, you can reclaim a significant amount of your upload capacity for the tasks that really matter.
Don't Forget Your Browser and System Drivers
Your web browser itself can be a major resource hog. Each open tab and every installed extension is a potential drain on your connection. Keeping dozens of tabs open isn't just a drain on your computer's memory; many of them are constantly sending and receiving small packets of data in the background.
Closing unnecessary background apps and browser tabs is one of the most effective ways to fix upload speed. Studies based on thousands of daily internet tests show multitasking can slash upload performance by an average of 35%, as these processes often consume a significant chunk of available bandwidth.
Out-of-date network drivers can also be a hidden source of trouble. These are the small bits of software that allow your computer's hardware to communicate with your network. Manufacturers release updates to fix bugs and improve performance, so it's always worth a quick visit to your computer or motherboard manufacturer’s website to make sure you have the latest version.
Finally, think about what you're actually uploading. Huge, uncompressed image files can take ages to send. Learning about the best image format for the web can help you dramatically shrink file sizes without a noticeable drop in quality, which is a lifesaver for anyone uploading photos or graphics.
Fine-Tuning Your Router and Network Settings
When unplugging cables and restarting devices doesn't do the trick, it’s time to roll up your sleeves and dive into your router’s software. Tucked away in these settings are some powerful tools that can give you direct control over your network's performance. With just a few targeted adjustments, you can often tell your router exactly how to manage its traffic and get your upload speeds back on track.
Think of your router as the traffic cop for your entire home network. Just like any computer, it runs on software called firmware, and manufacturers regularly release updates to fix bugs, patch security vulnerabilities, and improve overall stability. If your firmware is out of date, you could be dealing with performance bottlenecks that are silently sabotaging your upload speeds.
Getting into your router's settings is usually as simple as typing its IP address into a web browser. Once you're in, look for a section labeled "Firmware Update" or "Router Update" and follow the prompts. It's a quick fix that solves a surprising number of mysterious connection problems.
Prioritize Your Traffic with Quality of Service
One of the most powerful features buried in your router’s settings is Quality of Service, or QoS. This handy tool lets you tell your router which devices or applications are most important, ensuring they get the bandwidth they need, right when they need it.
It's like creating a VIP express lane for your internet traffic. For example, you can use QoS to give your work laptop top priority for that critical video call, even while someone else is streaming a 4K movie on the smart TV. This ensures your important uploads don't get choked out by less critical network activity.
Setting up QoS usually involves a few straightforward steps:
- Log into your router’s administrative dashboard.
- Find the QoS settings, which are often located under an "Advanced" or "Traffic Management" tab.
- Enable QoS and then select the devices or specific applications (like Zoom or Dropbox) you want to prioritize.
Modern routers often have simple, user-friendly interfaces for this—some even let you just drag and drop devices into a high-priority list. The result is that your most important upload tasks always get first dibs on your connection.
Configuring Quality of Service is one of the best ways to fix upload speed in a busy household. It stops less important devices from interfering with your critical uploads, creating a more stable and reliable connection for what matters most.
Ultimately, a good router is the foundation of a healthy home network. When you're trying to squeeze every bit of performance out of your connection, knowing how to choose a Wi-Fi router with modern features like Wi-Fi 6 and robust QoS is crucial. If your router is a few years old, it might just lack the features needed to properly manage today’s upload demands. In that case, a hardware upgrade might be the most effective solution.
Knowing When to Upgrade or Call Your ISP
So, you've tried everything. You've checked your hardware, shut down every background app, and even dug into your router settings, but your upload speed is still crawling. It’s frustrating, but it’s time to face the possibility that the problem isn't your gear—it's the internet plan itself.
There's only so much speed you can squeeze out of the connection you're paying for. Before you dial up your Internet Service Provider (ISP), make sure you have the data you've collected. Those baseline speed test results are your best ammunition for a productive conversation.
Asymmetrical vs. Symmetrical: The Real Bottleneck
For a lot of people, especially if you're on a traditional cable or DSL connection, the culprit is an asymmetrical connection. This is by design—your download speed is significantly faster than your upload speed. ISPs set things up this way years ago because most of us were consuming way more data than we were creating.
That model was fine for browsing websites or streaming Netflix, but it just doesn't cut it anymore. If you're a content creator, spend your days on video calls, or rely on cloud backups, that sliver of upload bandwidth can feel like a constant bottleneck.
The ultimate fix for a slow upload speed that’s baked into your plan is to switch to a symmetrical connection. These plans, usually from fiber optic providers, offer the same lightning-fast speeds for both uploading and downloading.
A symmetrical connection really is a game-changer. It gets rid of that artificial upload limit, letting you send huge files, stream high-quality video, and join video conferences without a hitch. It's the difference between waiting hours for a video to upload versus just a few minutes. Globally, fixed broadband upload speeds averaged only 51.49 Mbps in late 2024, a stark contrast to the 95 Mbps median download speed. This gap is precisely why many experience upload frustrations. In places like Singapore, where fiber is widespread, symmetrical speeds are common, making these issues a thing of the past. You can get a better sense of how different infrastructures stack up by looking at the global state of internet speeds and access.
Making the Call to Your ISP
When you get your provider on the phone, be prepared and get straight to the point. Don't start with a vague "my internet is slow." Instead, lead with your evidence.
Here's how that conversation should go:
- Share Your Data: Start by saying, "Hi, I've run several speed tests on a wired connection, and my upload speed is consistently around X Mbps, but my plan is advertised at Y Mbps."
- Ask for a Line Test: Request that they run a diagnostic on their end. Sometimes the problem is a signal issue or a network fault somewhere between their equipment and your home.
- Discuss Upgrades: If it turns out you're getting exactly what you pay for (and it's just not enough), then it's time to talk about a new plan. Be specific—ask if they offer any symmetrical or fiber optic plans in your area.
If they can't find a problem on their end and you're already on their best plan, it might be time to start looking for another provider who can give you the upload speeds you actually need.
Common Questions About Fixing Upload Speed
After running tests and trying a few fixes, it’s normal to have some lingering questions. Upload speed can be a tricky thing to nail down. Let's dig into some of the most common curiosities I hear from people trying to get their connection back on track.
Why Is My Upload Speed So Much Slower Than My Download?
This is probably the most common question I get, and the answer is simple: for most people, it’s by design. The internet infrastructure that most of us use (especially cable and DSL) was built on an "asymmetrical" model. It was engineered to heavily favor downloads because, for years, that’s what 99% of online activity was—browsing websites, watching videos, and downloading files.
But the way we use the internet has completely changed. Now we're all on video calls, live streaming, and constantly uploading huge files to the cloud. These activities demand a symmetrical connection, which is the signature feature of fiber optic plans. With fiber, you get the same blazing-fast speed whether you're uploading or downloading, which eliminates the bottleneck that older technologies were built with.
Can a VPN Reduce My Upload Speed?
Absolutely. In fact, a VPN will almost always slow down your connection to some degree, and uploads often take the biggest hit. When you switch on a VPN, your data has a much longer journey to make. First, it has to be encrypted on your device, then it gets sent to a remote VPN server (which could be across the country or the world), and only then does it head to its final destination.
This whole process of encryption and rerouting adds latency and overhead. Your connection has to do more work, and that work takes time, slowing things down.
To soften the blow, always try connecting to a VPN server that's physically closer to your actual location. Many modern VPN services also include a "split-tunneling" feature. This is a great tool that lets you decide which apps use the VPN and which ones can bypass it, giving your high-priority uploads a direct, faster route.
Does Wi-Fi Hurt Uploads More Than Downloads?
While a spotty Wi-Fi signal is bad for your entire internet experience, uploads are especially vulnerable to its instability. Think about it: when you're sending a file from your device, you need a steady, rock-solid signal. Any little hiccup caused by a wall, interference, or distance forces your device to stop, re-gather the lost data packets, and send them again. This stop-and-start process absolutely murders your upload speed.
Downloads, on the other hand, tend to be a bit more resilient. They can often buffer and better handle those tiny, split-second signal drops without you even noticing. This is exactly why a wired Ethernet connection is the gold standard for anything upload-heavy. For things like streaming or sending massive files, nothing beats the unwavering stability of a physical cable.
Will a New Router Guarantee Faster Uploads?
A new router can be a huge help, but it's not a silver bullet. It can only solve problems that are being caused by your current hardware being old, slow, or overwhelmed. A new router is like hiring a better traffic cop for your home network—it can direct the existing traffic more efficiently, but it cannot create more lanes on the highway.
In other words, a router can't generate more bandwidth than you're paying for in your internet plan. If your slow uploads are happening because your router is a five-year-old dinosaur, then yes, an upgrade is a fantastic idea. But if the bottleneck is your internet subscription itself, a brand-new router won't be able to break past that speed limit.
And if you’re constantly wrestling with large documents, our guide on the best free PDF converter software has some great tips for shrinking file sizes before you even hit the upload button.
ShiftShift Extensions puts a powerful Speed Test tool right in your browser, letting you instantly check your download, upload, and ping to see what's really going on with your connection. No need to open a new website—just click and test. It gives you the immediate feedback you need to troubleshoot like a pro. Learn more and get a smarter workflow at https://shiftshift.app.